Mario Aguilera, UC San Diego
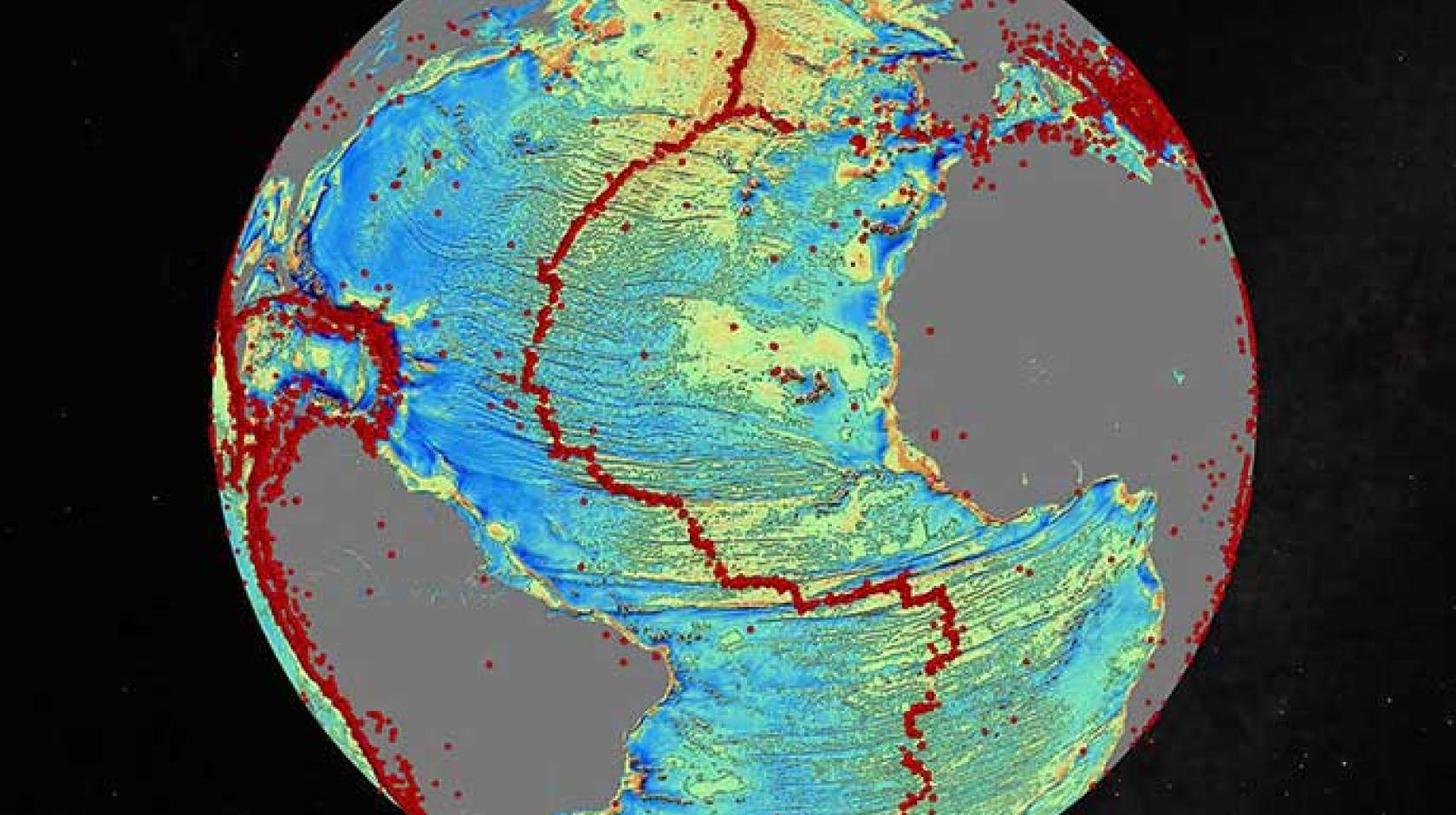
Accessing two previously untapped streams of satellite data, scientists at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego and their colleagues have created a new map of the world’s seafloor, creating a much more vivid picture of the structures that make up the deepest, least-explored parts of the ocean. Thousands of previously uncharted mountains rising from the seafloor and new clues about the formation of the continents have emerged through the new map, which is twice as accurate as the previous version produced nearly 20 years ago.
Developed using a scientific model that captures gravity measurements of the ocean seafloor, the new map extracts data from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) CryoSat-2 satellite, which primarily captures polar ice data but also operates continuously over the oceans, and Jason-1, NASA’s satellite that was redirected to map the gravity field during the last year of its 12-year mission.
Combined with existing data and drastically improved remote sensing instruments, the new map, described in the journal Science, has revealed details of thousands of undersea mountains, or seamounts, extending a kilometer or more from the ocean bottom. The new map also gives geophysicists new tools to investigate ocean spreading centers and little-studied remote ocean basins.
“The kinds of things you can see very clearly now are abyssal hills, which are the most common land form on the planet,” said David Sandwell, lead scientist of the paper and a geophysics professor in the Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics (IGPP) at Scripps.
The authors of the study say the map provides a new window into the tectonics of the deep oceans. Previously unseen features in the map include newly exposed continental connections across South America and Africa, and new evidence for seafloor spreading ridges at the Gulf of Mexico that were active 150 million years ago and are now buried by mile-thick layers of sediment.
“One of the most important uses of this new marine gravity field will be to improve the estimates of seafloor depth in the 80 percent of the oceans that remains uncharted or is buried beneath thick sediment,” the authors say in the report.
“Although CryoSat-2’s primary mission is in the cryosphere, we knew as soon as we selected its orbit that it would be invaluable for marine geodesy, and this work proves the point,” said Richard Francis, a coauthor of the paper and project manager for the development of CryoSat-2 at the European Space Agency, and honorary professor in the Department of Earth Sciences at University College London.
The new map also provides the foundation for the upcoming new version of Google’s ocean maps to fill large voids between shipboard depth profiles.
“The team has developed and proved a powerful new tool for high-resolution exploration of regional seafloor structure and geophysical processes,” says Don Rice, program director in the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Division of Ocean Sciences. “This capability will allow us to revisit unsolved questions and to pinpoint where to focus future exploratory work.”
“The use of satellite altimeter data and Sandwell’s improved data processing technique provides improved estimates of marine gravity and bathymetry world-wide, including in remote areas,” said Joan Cleveland, Office of Naval Research (ONR) deputy director, Ocean Sensing and Systems Division. “Accurate bathymetry and identifying the location of seamounts are important to safe navigation for the U.S. Navy.”
In addition to Sandwell and Francis, coauthors of the paper include R. Dietmar Muller of the University of Sydney, Walter Smith of the NOAA Laboratory for Satellite Altimetry, and Emmanuel Garcia of Scripps.
The study was supported by NSF, ONR, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, and ConocoPhillips.